A car’s catalytic converter is a vital part of a vehicle that helps regulate the emissions from a car’s engine. But if your car is stalling, can a bad catalytic converter cause the vehicle to shut off?
Usually, a faulty catalytic converter would not be the reason for a car to turn off unless the catalytic converter is really badly damaged. However, the car would already be undrivable anyway.
In this article, I’ve included information on the times when a catalytic converter could cause the car to shut off and the signs you should look out for that it is failing so you may never have to worry about a catalytic converter getting so bad it causes your car to stall.
What Is a Catalytic Converter, and How Does It Function?
A catalytic converter is a component in a car’s exhaust system. It changes the toxic and lethal gasses a vehicle generates into less fatal gasses, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide, before releasing them through the exhaust muffler into the atmosphere. The catalytic converter contains various valuable metals such as palladium, platinum, and rhodium arranged into a honeycomb through which the exhaust gases pass.
There are other ways to remove hydrocarbons from some cars’ exhaust emissions, such as a DPF filter and an EGR valve. A catalytic converter alongside an EGR valve on a petrol engine is the perfect combination to remove toxic gasses and meet emissions regulations. You can read more on the function of a catalytic converter here.
Can a Bad Catalytic Converter Cause the Car to Shut Off?
A bad catalytic converter can cause a car to shut off, but this only happens if the blockage is severe enough to let virtually no gases pass through. In such cases, the ECU (engine control unit) compensates for the blockage by increasing the amount of fuel and air injected into the engine.
To determine the catalytic converter’s performance, the ECU uses oxygen sensors to measure oxygen levels in exhaust gases before and after. However, if the blockage is extreme, the increased back pressure in the exhaust and the lack of fresh oxygen for ignition can cause the car to shut off. It’s important to note that these are extreme circumstances, and you would already be aware of an issue with the vehicle if you continued to drive with a severely clogged catalytic converter.
A Failing Catalytic Converter
In other cases, a car with a failing catalytic converter might start without any problem, but it might stall, feel like it is about to stall, and run rough. This won’t necessarily be the catalytic converter’s fault but one of the supporting components reacting. The oxygen sensors will detect the underperforming catalytic converter and try to compensate by adding more fuel and oxygen, causing a misfire. Driving with a misfire is a considerable risk as the car could go into limp mode, or the engine can shut down at any time. The engine shut-off might happen when you are already driving.
To avoid getting caught off guard, if you notice a fault or the engine management light illuminating when you start the vehicle, be cautious before speeding off the road.
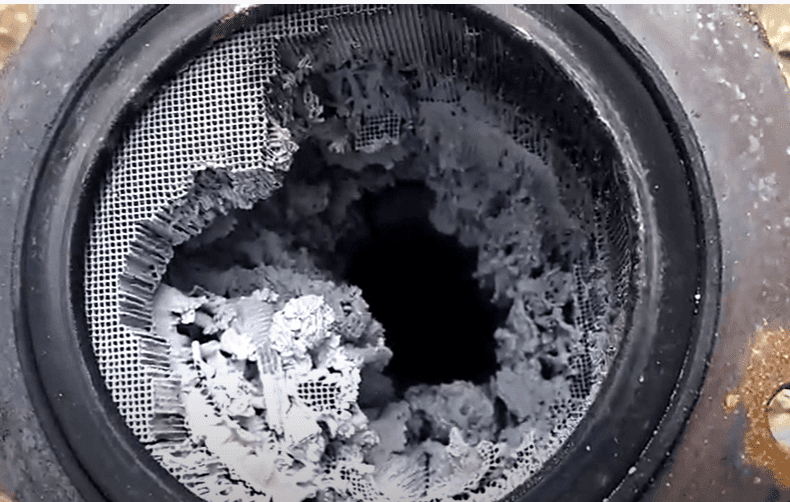

Signs of a Failing Catalytic Converter
Certain signs indicate a catalytic converter is failing and may need replacing; they include:
- Decrease In Engine Performance
One of the easiest signs to recognize, indicating that a car’s catalytic converter requires replacement, is a reduction in engine performance. Usually, this comes in the form of excessive fuel being pumped into the car engine, an increase in exhaust pressure, the engine light coming on, weak rates of acceleration, and reduced all-around top speed.
- Reduction In Fuel Efficiency
A failing catalytic converter can also severely reduce your vehicle’s overall fuel efficiency because your engine cannot filter its emissions fast enough. As it is not functioning in perfectly optimal conditions, your car will consume more fuel to produce the same amount or less power. Suppose you notice that you often go to the gas station regularly despite little or no alterations in your driving habits. In that case, your catalytic converter could be the issue.
- Rattling Noises
An unusual rattling sound from your car’s exhaust system, particularly when you turn on the ignition or while driving at high speed, can mean the catalytic converter internals may be damaged. Occasionally, it could just be a loose screw connecting the exhaust system, a heat shield loose, or a broken hanger bracket, which could be an easy and economical fix. Worse, it could be a breakdown of the catalytic honeycomb in your catalytic converter due to age or a poor-quality aftermarket version. Therefore, it needs to be replaced as soon as possible.
- Start-Up And Stalling Issues
With a severely clogged catalytic converter, gasses can pile up and choke out your engine. This can cause a sudden shutdown of your car’s engine or refusal to restart. This could prove dangerous, as your car could turn off while driving. As such, seek repair immediately.
- Constant Misfires
If your car is undergoing endless misfires while in motion, you should have a mechanic look at its catalytic converter. However, misfires aren’t caused by the car’s catalytic converter directly but by the supporting components. But bear in mind that misfires will damage the catalytic converter.
- Unusual smells
A catalytic converter that has an unusual rotten egg smell has usually failed. Its job is to convert the tiny amount of sulfur in gas into an odorless gas. Sulfur smells eggy when burning, so if you can smell egg, the catalytic converter is not doing its job.
What Causes a Catalytic Converter to Fail?
The most common reasons for a catalytic converter failing include:
1. Overheating due to engine misfires or a rich fuel mixture, usually caused by a failed sensor.
2. Physical damage to the catalytic converter.
3. Contamination from oil or coolant, most probably caused by overfilling engine oil or a failed head gasket.
4. Wear and tear over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does A Catalytic Converter Last?
The lifespan of a catalytic converter can vary depending on several factors, such as driving habits and the quality of the part itself. On average, a catalytic converter lasts around 100,000 miles.
Can A Clogged Catalytic Converter Damage The Engine?
A clogged catalytic converter could damage the engine. When the catalytic converter becomes clogged, exhaust gas flow is restricted, which can cause increased back pressure in the engine. This increased pressure can cause damage such as a cracked or warped cylinder head, damaged pistons or valves, and even a blown head gasket.
To Summarise
The catalytic converter is not just important to the environment as it prevents the emission of lethal gasses into the air; it also ensures the smooth running of a car engine. Therefore, it should be kept in reasonably good condition. When a catalytic converter becomes badly damaged, it can cause a vehicle to shut off, although this is rare and usually the last failure stage. If you discover an issue with yours, endeavor to fix it as soon as possible.